Understanding Patient Monitoring: Spot Monitors vs. Vital Signs Monitors
Patient monitoring plays a crucial role in providing quality care across all medical specialties. From general practitioners to cardiologists, accurate patient data is vital for effective treatment and diagnosis. While both spot monitors and vital signs monitors help gather this essential information, they serve different purposes and offer distinct functionalities.
In conversation, we distinguish between a spot monitor and a vital signs monitor. So what are the actual differences?
Spot Monitors: Quick Checks and Initial Assessments
Think of a spot monitor as a camera taking a snapshot of your patient's health at a specific moment. These devices provide single measurements of vital signs, offering a glimpse into the patient's current condition. Typical features of a spot monitor include:
- Pulse oximetry: Measures blood oxygen saturation.
- Non-invasive blood pressure: Provides blood pressure readings without needles.
- Thermometry: Measures body temperature using various methods (oral, axillary, or infrared).
Common Uses
Spot monitors are ideal for quick check-ups, initial consultations, and routine assessments where continuous monitoring isn't necessary. Their portability and ease of use make them valuable tools in various healthcare settings.
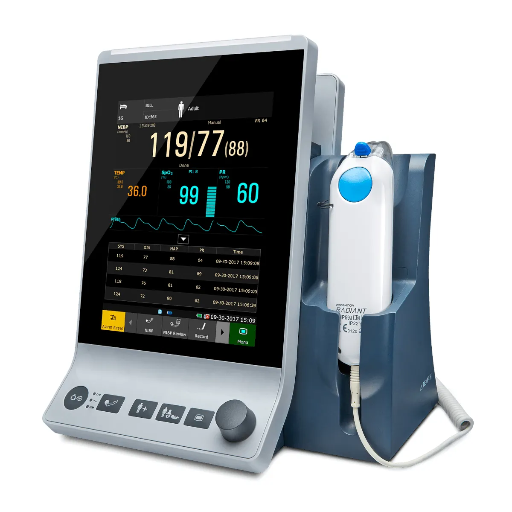
A spot monitor
Key Features
- Single measurements: Capture vital signs at a specific point in time.
- Portability: Many models offer mobile stands or wall-mounting options for easy transport and storage.
- EMR/Patient Record Integration: Some devices can connect with electronic medical record systems for seamless data transfer.
Vital Signs Monitors: Continuous Monitoring for Critical Situations
In contrast to spot monitors, vital signs monitors provide ongoing, real-time data about a patient's vital signs. These devices are essential for situations requiring constant vigilance and immediate intervention. They are commonly used in:
- Surgical procedures: Monitoring vital signs during operations.
- Post-operative recovery: Tracking patient stability after surgery.
- Intensive care units: Closely observing critically ill patients.
- IV medication administration and dialysis: Monitoring patient responses to treatments.
Advanced Features
Vital signs monitors often include more advanced functionalities, such as:
- ECG (Electrocardiogram): Measures heart activity.
- Invasive blood pressure monitoring: Provides continuous and precise blood pressure readings through a catheter.
- Audible alarms: Alert healthcare providers to critical changes in vital signs, enabling rapid response.
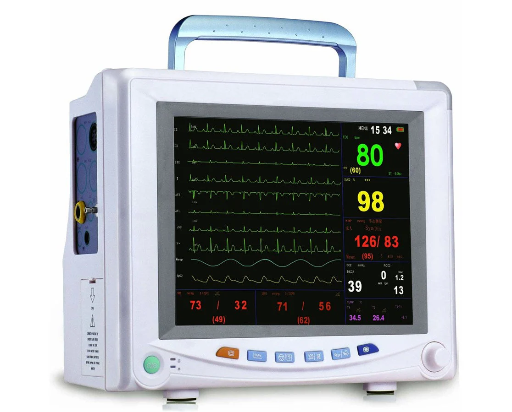
A continuous patient monitor
Key Features
- Continuous monitoring: Provides real-time data on patient vital signs.
- Advanced measurements: Includes ECG and invasive blood pressure monitoring for comprehensive assessments.
- Alarm systems: Triggers alerts when vital signs reach critical levels.
- EMR/Patient Record Integration: Seamlessly integrates with electronic medical record systems.
Choosing the Right Monitor
The choice between a spot monitor and a vital signs monitor depends on the specific needs of your clinical practice and the level of monitoring required for your patients. By understanding the differences between these two types of devices, you can make informed decisions to enhance patient care and safety.
If you have inquiries and questions, write to us at sales@lhmeds.com or call us at (441) 705-5483.